FAIR Data and Collaborative Workflow for R&D
Published on May 12, 2025 — 3 min read
In the push toward digital transformation in R&D, making experimental data FAIR (Findable, Accessible, Interoperable, and Reusable) is no longer optional. Structured, well-documented, and shareable data reduces duplication, promotes collaboration and drives innovation more efficiently across the research pipeline.
But embracing FAIR as a guiding principle is only the first step. In practice, many R&D organizations still struggle to implement it: Data often remains trapped in proprietary formats, poorly documented, or isolated in personal folders and disconnected systems.
A recent article on Chemical Science (Herrmann et al. "Enhancing FAIRdata by providing digital workflows from data generation to the publication of data: an open source approach described for cyclic voltammetry†", Chem. Sci., 2025, 16, 4430) offers a practical example of how to overcome these challenges. Focusing on cyclic voltammetry (CV) experiments, the team developed a complete, open-source workflow to make lab data FAIR, from data capture to repository deposition, offering a blueprint for how R&D teams can translate FAIR principles into action.
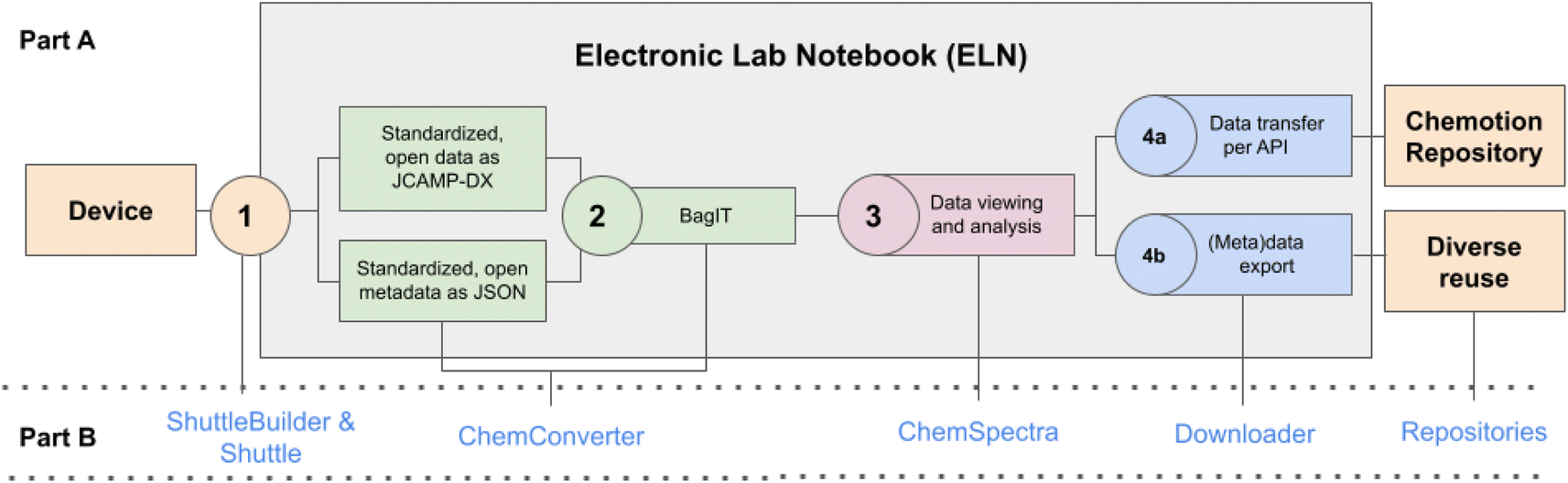
Below are the key steps of their workflow:
Automate Data Transfer from Instruments to ELN
To ensure that raw data is consistently captured at the point of generation, the authors developed a system for automated data transfer from lab instruments to electronic lab notebook (ELN), using a flexible tool called ShuttleBuilder. ShuttleBuilder was designed to work with a wide range of lab instruments and setups, making it easy to automate data collection across different analytical labs.
Standardize Data and Metadata Conversion
Lab instruments often produce data in proprietary formats tailored to the vendor’s software hampering data reuse. To address this, the authors created a tool called ChemConverter to transform raw data into open, interoperable formats. ChemConverter uses device-specific profiles to define how to interpret and convert each instrument’s output, and enables consistent data formatting and metadata extraction across multiple vendors.
Integrate Visualization and Analysis
Once converted, the data and metadata are bundled as BagIt archive files and visualized using ChemSpectra, a tool allowing detailed inspection of CV results and identification of key metrics. Similarly, other visualization or analysis may be integrated to support other types of instrument data.
Automate Data Publishing to Repositories
After annotation and review, the finalized datasets can be published to open repositories (e.g. Zenodo), or internal enterprise data hubs, depending on the context. The step makes the data findable and accessible to others, while preserving metadata and provenance to ensure it remains reusable across institutions, instruments, and research teams.
This end-to-end workflow illustrates that FAIR data is achievable by R&D teams with the right tools and processes. By tackling challenges across the data lifecycle, it demonstrates how experimental data can be captured, standardized, analyzed, and shared in a reusable format. For R&D teams on their FAIR journey, what challenges have you encountered, and what’s worked well so far?
- FAIRData ManagementCollaboration